Acoustic Treatment vs. Furniture
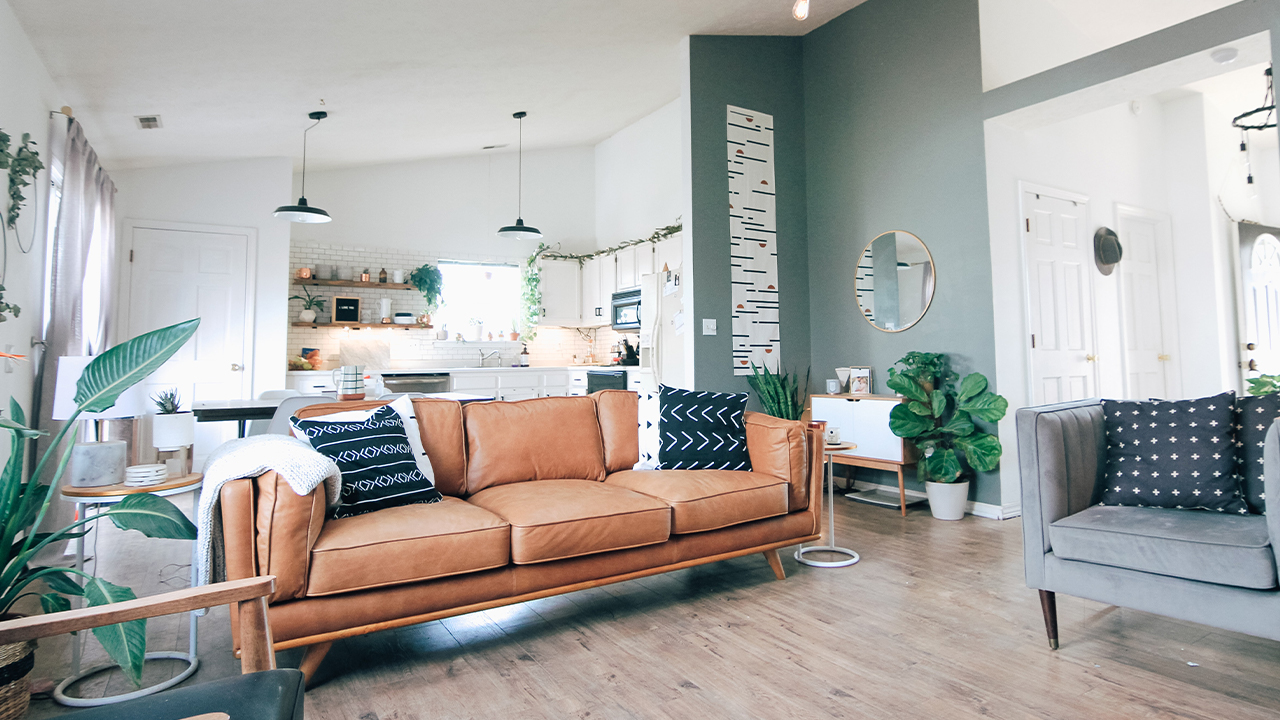
Acoustic treatment vs furniture are opposite terms. Furniture is designed to provide storage for objects such as cabinets and seats to sit upon when watching a movie or having tea. Acoustic treatment is designed to absorb or diffuse energy. Each has its own function and there is some overlap in those functions but not in a predictable and consistent manner. In acoustics, we have 2 technologies that we use to manage energy within our rooms. We have sound absorption technology along with sound diffusion technology. Let’s examine both technologies, so we can have an understanding of the acoustic treatment vs. furniture debate.
Sound Absorption
Sound absorption technology is designed to absorb excess energy. The technical term for this is amplitude. The goal of any sound absorption technology is to reduce the strength or amplitude of certain frequencies. We have low, middle, and high-frequency energy that needs to be absorbed within our rooms. Low-frequency energy requires special technology to absorb the long waves of energy below 100 Hz. Low-frequency energy absorption requires technology that is 8 – 16″ deep and has mass and density. Middle and high-frequency energy can be absorbed using technologies that are thinner in their depths and lighter weight due to the shorter wavelengths.

Sound Diffuser
Sound Diffusion
Diffusion is a technology that reduces the impact of reflections on our wall surfaces. Diffusers are a technology that makes a small room sound larger. Diffusers that create sound diffusion are a complicated structure that requires many variables to be honored in order to create what we call a diffuse sound field. Diffusers require that we calculate the distance from the listener to the wall surfaces and assign the correct diffusion sequence that will work within that distance and room usage. The frequency response of the diffuser will have to be calculated to match the room usage and the distances involved within the room.
Furniture Absorption
In the acoustic treatment vs furniture debate, it is difficult to find furniture than can achieve the performance objectives of both diffusion and absorption. Furniture such as couches can absorb some lower frequency energy but most lack the ability to absorb enough energy to have an audible impact. They are simply not designed for an absorption function. Draperies can be used to absorb middle and high-frequency energy depending on the thickness of the drapes. Multiple layers of materials in the drapes will increase the rate of absorption since the thickness or depth of any sound absorptive material increases both the rate and level of absorption. The rate of absorption is how fast the energy is absorbed at each frequency and the level is how low that material will go in its absorption. The thicker the drape, the lower frequencies it will absorb at and the more of each frequency it will absorb.

Sound Diffusers in a Home Theater Room
No Furniture Diffuser
Taking this acoustic treatment vs. furniture debate into sound diffusion would require that a piece of furniture be able to satisfy the requirements necessary to create a diffused sound field. There are 5 criteria that must be honored if true sound diffusion is required. First, there can be no spatial irregularities in frequency response within the room. There can be no beats in the decay rates within the room. This decay rate must be exponentially smooth and be the same in all room locations. Finally, the reverberation times within the room must be the same in all room locations. As you can see by the requirements of diffusion, it would be impossible for a piece of furniture to handle all of these criteria.
Reverberation: https://www.cirrusresearch.co.uk/blog/2018/04/what-is-reverberation-time-and-how-it-is-calculated/
Reverberation
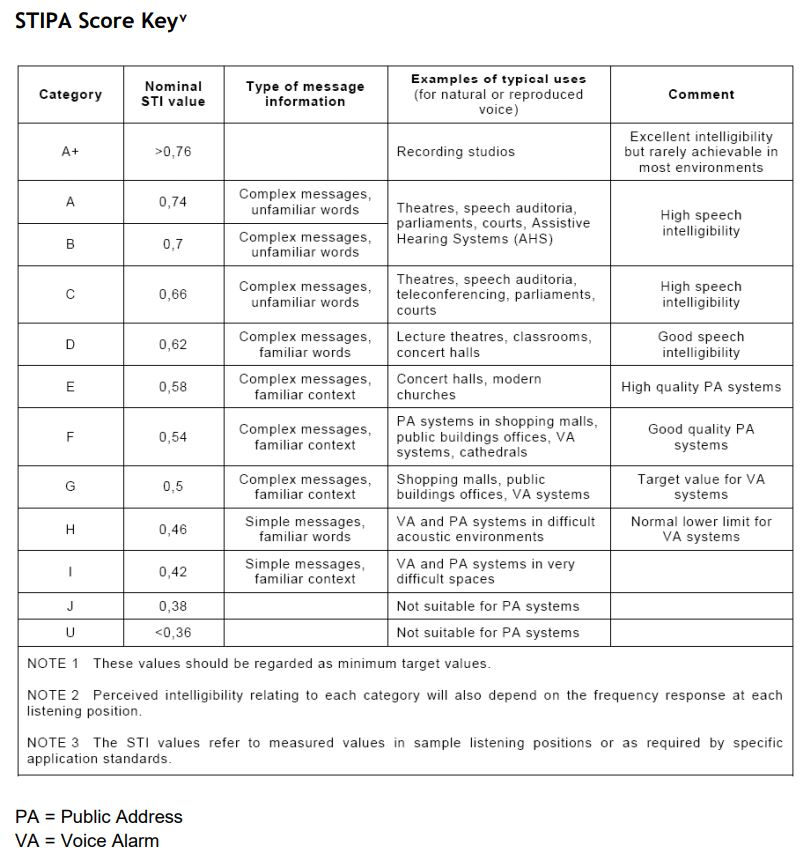
Most rooms suffer from what we call high reverberation times. Reverberation is the ability of sound to “hang” around within the room after the sound has stopped being produced. Reverberation times are calculated by adding up the reflections from all the wall surfaces. High reverberation times are often referred to as echo. The echo is a repetition of a sequence of frequencies. The issue we must deal with in rooms is high reverberation times. Reverberation is a form of room distortion that impacts our ability to hear speech clearly in rooms. Since reverberation is room distortion it has a negative impact on speed intelligibility.
Speech Intelligibility: https://journals.lww.com/thehearingjournal/Fulltext/2004/10000/The_Speech_Intelligibility_Index__What_is_it_and.3.aspx
Speech Intelligibility
Speech intelligibility is an index we use to measure how many words we can hear in a sentence when that sentence is spoken within our rooms. Reverberation or reflections from our room boundary surfaces can have a negative impact on our ability to hear words that are spoken. Our room walls and furniture within the room all contribute to reflections. These reflections when you add them all together are room distortion. Room distortion interferes with our speech intelligibility or how many words we can hear within a sentence that is spoken by a person or music that is played.
Room Hard Surfaces
If we have a typical room where there are windows and hard surface areas such as tile floors and even drywall we will have reflections. The amount of reflections we will have is based upon the surface area of the hard surfaces within our rooms. If we have large surface areas such as tile floors, we will have to have equal surface areas of softer materials that absorb energy that is based in the middle and high-frequency ranges. If we have 100 square feet of tile on our floors then we will need at least 150 square feet of sound absorption materials within the room. This treatment task will be difficult to achieve without the addition of other sound absorption treatments that are specifically designed for sound absorption speech frequency ranges. A popular treatment technology to use to manage speech intelligibility is open-celled foam.
Acoustic Fields Foam Panel: https://www.acousticfields.com/product/acoustic-panels/

Foam Panel
Open – Celled Foam
Recording studios, live recording rooms, home theaters all require sound absorption technologies for low, middle, and high frequencies. Special foam technologies are used to manage excess energy within these critical listening environments. We have developed an acoustic foam technology that was designed for speech and music. It has the proper rates and levels of absorption that reduces just enough of the reflected energy to clean up our speech intelligibility within our rooms. The foam technology can be placed within a wooden cabinet that is fabric covered to match the decor of the room. Units can be hung on the wall surfaces to absorb the reflected energy and minimize high reverberation times and increase our ability to hear more clearly within our rooms.
Acoustic Treatment vs. Furniture
In the acoustic treatment vs furniture debate, we can see that absorption treatment to lower reverberation times can be achieved with some furniture such as drapes and couches. However, to really go after the speech intelligibility issues you need to cover large amounts of surface area and the drapes will not have enough surface area coverage to treat the reflections that occur from our tile floors and walls. Additional treatment will have to be installed to increase the coverage of surface areas to minimize the reflections from tile floors, walls, furniture, and windows.
About Us At Acoustic Fields: https://www.acousticfields.com/about/